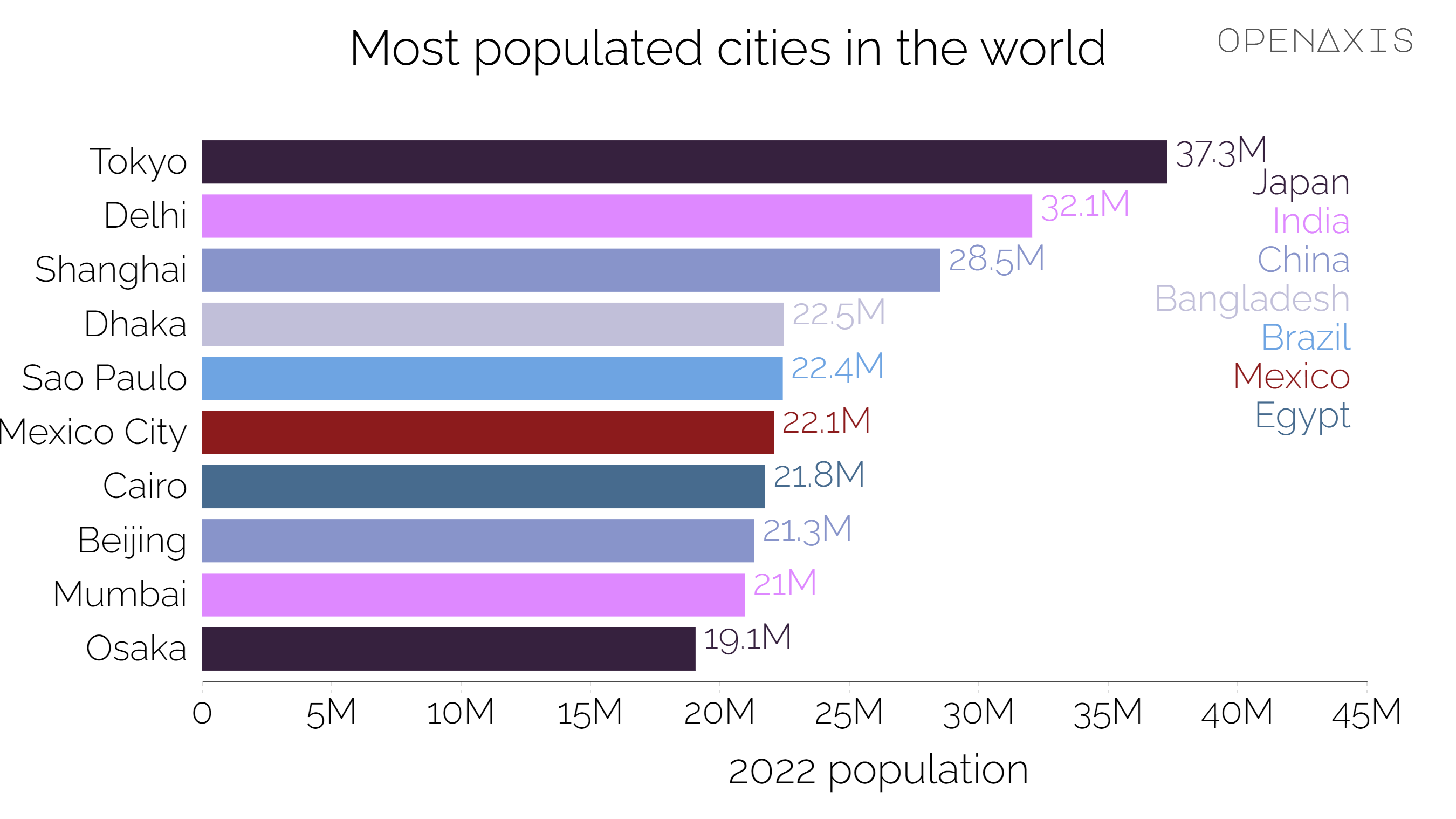
It is perhaps unsurprising that the majority of the most populous cities in the world are in the two most populated countries in the world, China and India. Among these are Shanghai and Beijing, with populations of 25 and 22 million respectively, Delhi (27 million), and Mumbai (over 21.5 million).
However, Tokyo is the largest city in the world if the entire Tokyo metro area is included, with a total of more than 38 million residents. Another Japanese city, Osaka, also has a very large population of almost 20.5 million.
Source: United Nations - World Urbanization Prospects
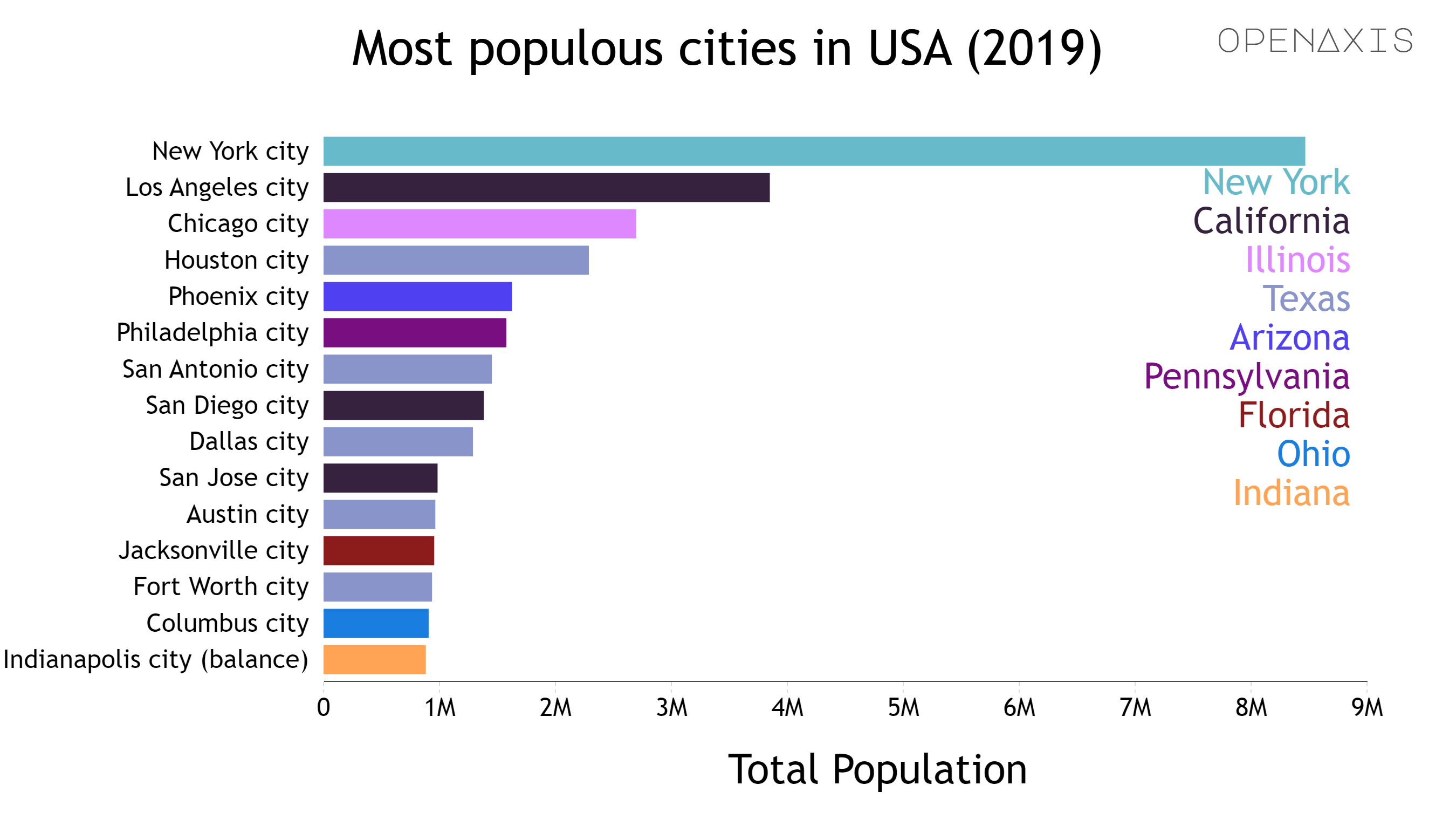
The top 15 largest cities remained the same as in 2020 although more than half experienced decreases in their population between 2020 and 2021: New York, New York (-305,465); Los Angeles, California (-40,537); Chicago, Illinois (-45,175); Houston, Texas (-11,777); Philadelphia, Pennsylvania (-24,754); San Diego, California (-3,783); Dallas, Texas (-14,777); San Jose, California (-27,419); and Indianapolis, Indiana (-5,343).
Despite decreasing in population, New York remained the nation’s largest city. Its July 1, 2021, population of 8.5 million was more than twice that of the next largest city, Los Angeles, with a population of nearly 4 million.
Source: US Census Bureau
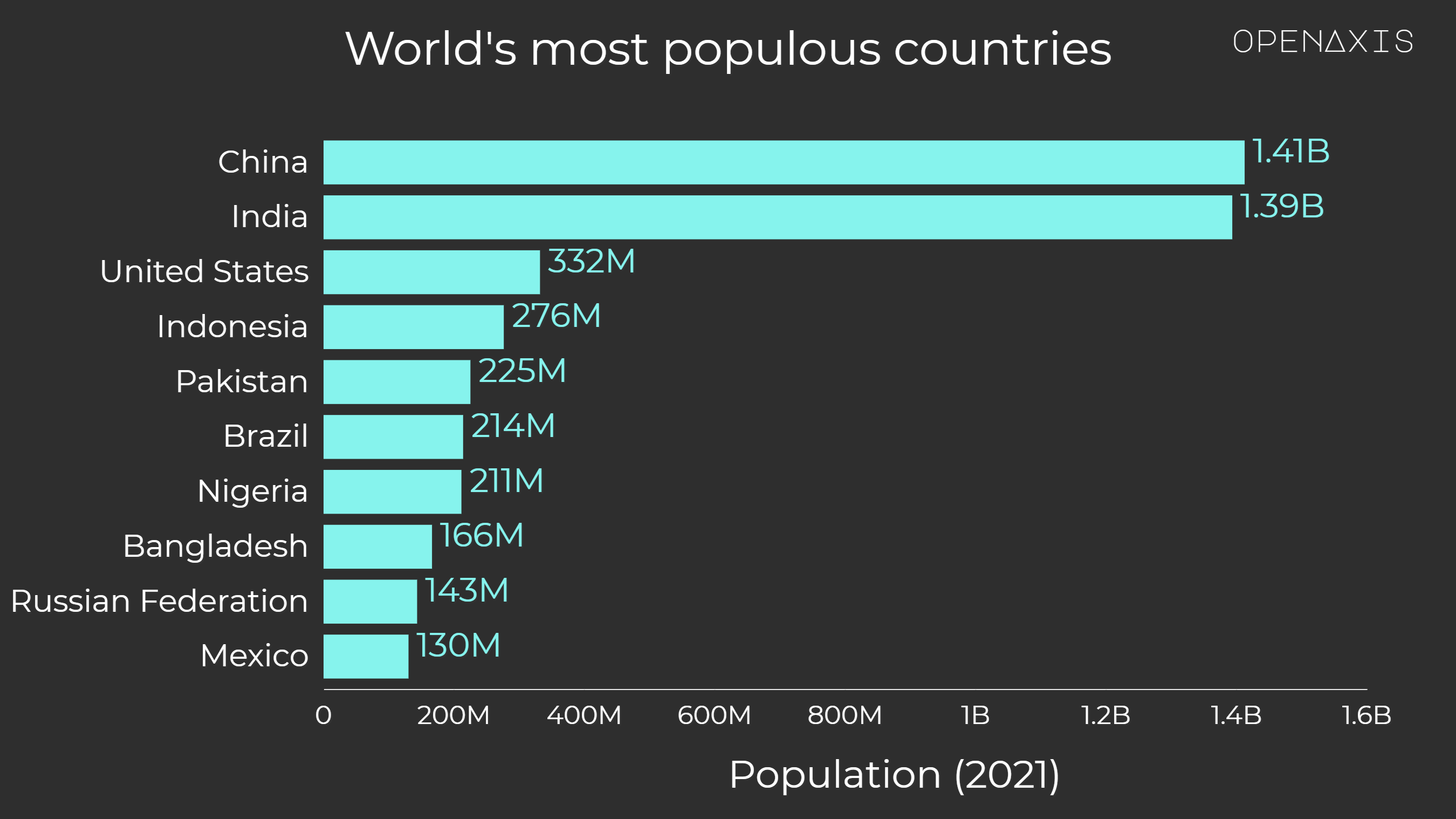
Total population is based on the de facto definition of population, which counts all residents regardless of legal status or citizenship. The values shown are midyear estimates. Dataset includes population figures from 1960-2021.
Source: World Bank
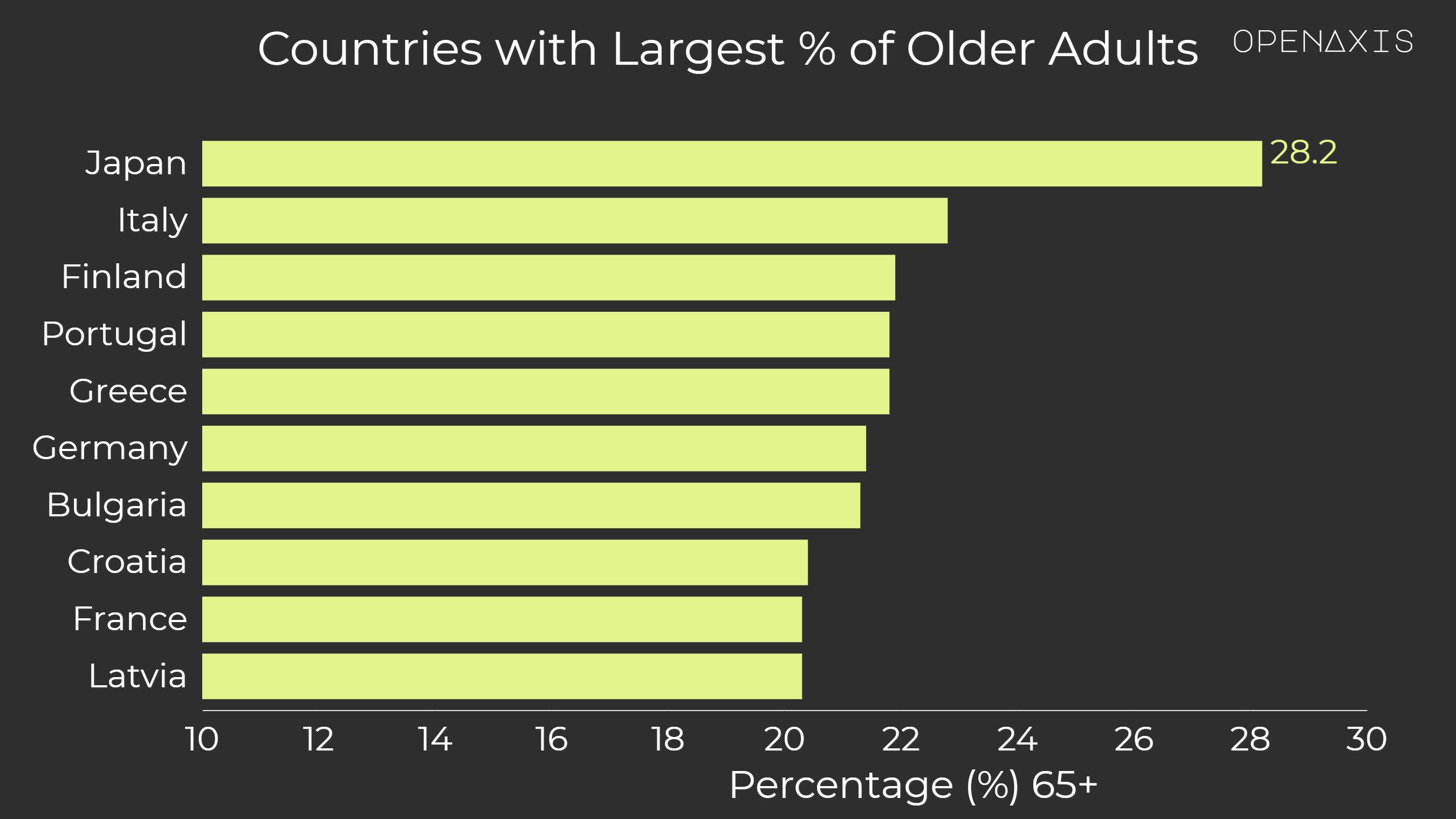
Asia and Europe are home to some of the world’s oldest populations, those ages 65 and above. At the top is Japan at 28 percent, followed by Italy at 23 percent. Finland, Portugal, and Greece round out the top five at just under 22 percent.
Southern Europe, which includes such countries Croatia, Greece, Italy, Malta, Portugal, Serbia, Slovenia and Spain, is the oldest region in the world with 21 percent of the population ages 65+.
Twelve percent of China’s population is age 65 or above. That share is 16 percent in the United States, 6 percent in India, and 3 percent in Nigeria.
Source: PRB, United Nations